A World-Leading Centre for Predictive in vitro Model Research, Training and Translation
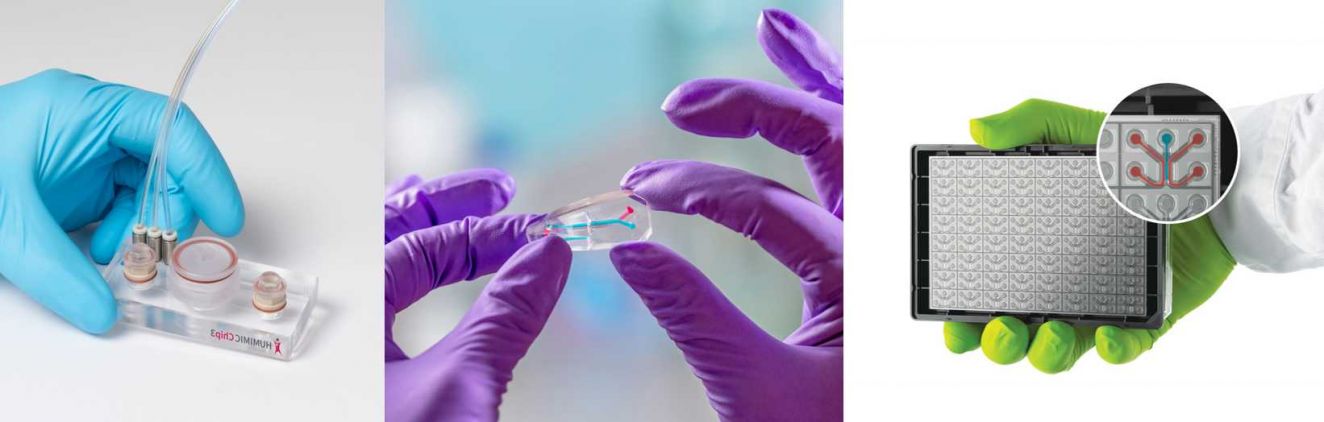
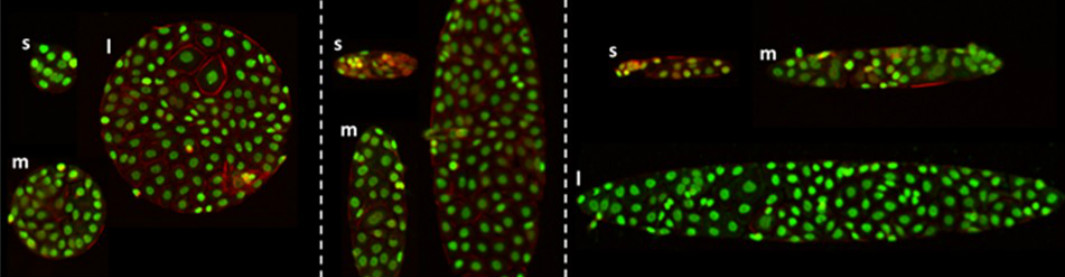
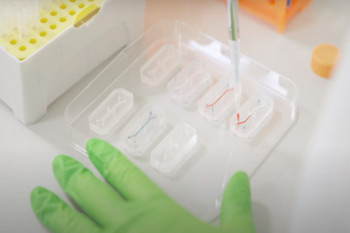
Research with the Centre incorporates a wide range of model systems including 2D and 3D cell culture models, organoids, microphysiological systems, organ-on-a-chip technology, Non Animal Methods (NAMs), and other types of in vitro model.
With approximately 100 academic staff across the Faculty of Science and Engineering and the Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary's Centre for Predictive in vitro Models is leading development and use of these complex in vitro models in partnership an extensive list of partners and industry affiliates.
Queen Mary provide leadership in this field hosting the annual UK symposium and engaging with Government, policy makers, funders, industry and other stake holders to support development and adoption of this transformative technology.
Events
 Wed 25 Mar 2026 Wed 25 Mar 202615:00 - 16:00 | CPM Seminar Series - Dr Francesco Tedesco |
 Wed 22 Apr 2026 Wed 22 Apr 202615:00 - 16:00 | Seminar: CPM Seminar Series - Dr Mattea Finelli (University of Nottingham) |
 Wed 20 May 2026 Wed 20 May 202615:00 - 16:00 | CPM Seminar Series - Dr Bin Zhang (Brunel University) |
Recent Publications
- Neuromodulation of a peripheral nerve using fully polymeric cuff electrodes: Understanding predictability of selective stimulation.
Journal of Neural Engineering, Iop Publishing
11-02-2026 - DOP078 Development of a bioengineered 3D model of gut barrier defence against Candida albicans invasion and inflammasome activation in Crohn’s Disease
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis, Oxford University Press (Oup) vol. 20 (Supplement_1)
01-01-2026 - Development and characterization of an on-chip glioma outgrowth model
Daoud JPA, Collisson AE, Asaid D, do Couto Lopes EC, Paraskevopoulos D, Chapman CAR
In Vitro Models, Springer Nature, 1-13.
08-12-2025
Recent Grants
- COaCT - Development of a vascularised muscle-tendon inflammation-on-a-chip model
Hazel Screen and Martin Knight
£166,623 UCB Pharma SPRLGrant Summary
01-10-2025 - 30-09-2029 - COaCT- A multi-organ model for breast cancer metastasis to bone and liver
Martin Knight
£46,623 CN-Bio Innovations Ltd
01-10-2025 - 30-09-2029 - Role of the mechano-lipid matabolic signalling axis in cardiovascular disease
Thomas Iskratsch, Nicolae Radu Zabet and Qingzhong Xiao
£919,939 British Heart FoundationGrant Summary
01-10-2025 - 30-09-2030